Microsoft Excel is one of the most popular tools for handling data. From students to professionals, almost everyone uses it to organize, analyze, and present information. Among its many features, tables are one of the easiest yet most useful tools.
Whether you’re managing a monthly budget or tracking sales, tables make your data neat, structured, and easy to work with.
In this guide, you’ll learn everything about basic tables in Excel—what they are, how to create them and how to make the most of their features.
What is a Table in Excel?
A table in Excel is simply a structured range of related data. Once you convert your data into a table, Excel automatically gives you powerful tools such as:
- Ready-made formatting styles
- Easy sorting and filtering
- Automatic expansion when you add new data
- Simple, readable formulas with column names instead of cell references
In short, tables save time and make your work much more organized.
How to Create a Table in Excel:
Creating a table is quick and easy. Here’s how you can do it:
- Select the range of data you want to convert.
- Example: A1:D10
- Go to the Insert tab on the ribbon and click Table.
- In the dialog box, check “My table has headers” if your data already includes column names.
- Click OK.
That’s it. Your data is now converted into a table with filters and formatting applied automatically.
Keyboard shortcut: You can also press Ctrl + T on your keyboard to create a table instantly.
Step-by-Step Example:
- Prepare Your Data
- Enter your data in rows and columns.
- Make sure each column has a header (like Name, Sales, Date).
- Avoid blank rows or columns inside the data range.
Example:

- Select the Data Range
- Highlight the range of cells you want to turn into a table.
Example: A1:C4
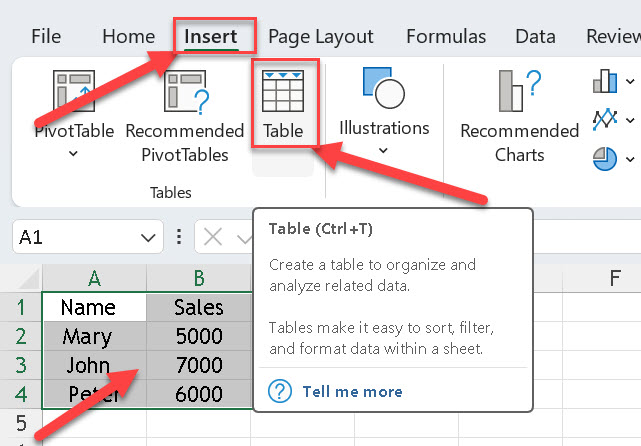
- Insert a Table
- Go to the Insert tab on the Ribbon.
- Click Table.
- Confirm the Table Range
- A dialog box appears with the selected range.
- Check the box “My table has headers” if your data already includes column headings.
- Click OK.

Now, your data is officially a table.

Key Features of Excel Tables:
1. Table Styles
- Select your table, and you’ll see a new Table Design tab.
- You can choose from different color styles to make your table stand out.
- Options like Banded Rows, Banded Columns, Header Row, and Total Row improves readability.

2. Sorting and Filtering
- Each column header has a drop-down arrow.
- You can quickly sort data (A to Z, or Z to A).
- Or filter it to display only specific values.

3. Total Row
- In the Table Design tab, check the option Total Row.
- A new row will add at the bottom where you can apply functions like SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MAX and MIN automatically without writing formulas manually.


4. Cell References:
Instead of using cell references like =SUM(B2:B10), You can use column names directly:
Example:
=SUM(Table1[Sales])
This makes formulas easier to read and understand.
5. Automatic Expansion
When you add a new row or column next to a table, Excel will automatically extend the table with the same formatting and formulas.
Common Things You Can Do with Tables:
Adding or Removing Columns/Rows
- Just type data next to your table and Excel extends it.
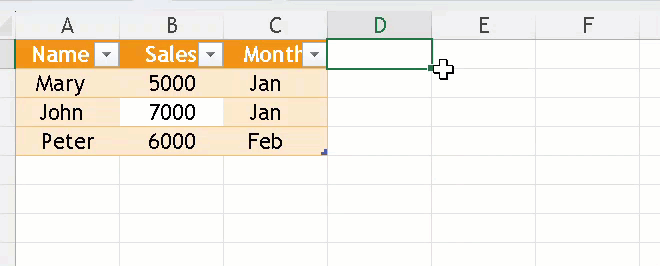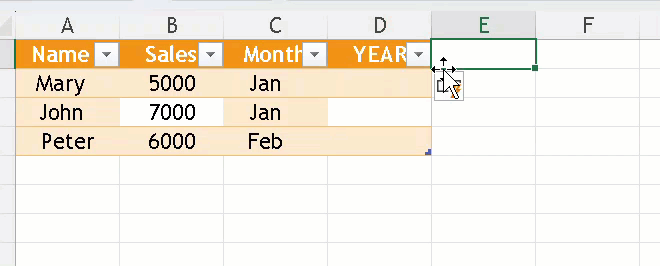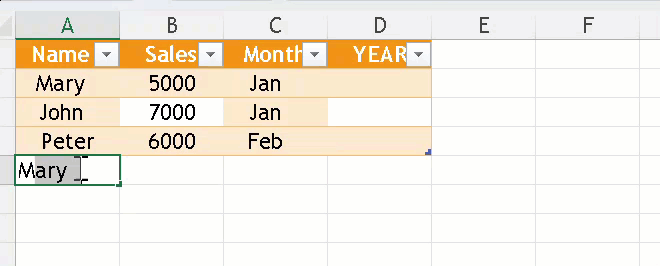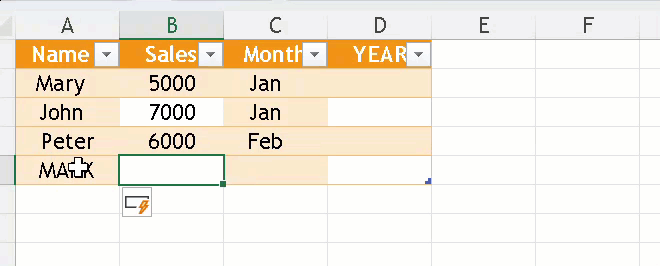
- Or Right-click on a row/column to Insert or Delete.

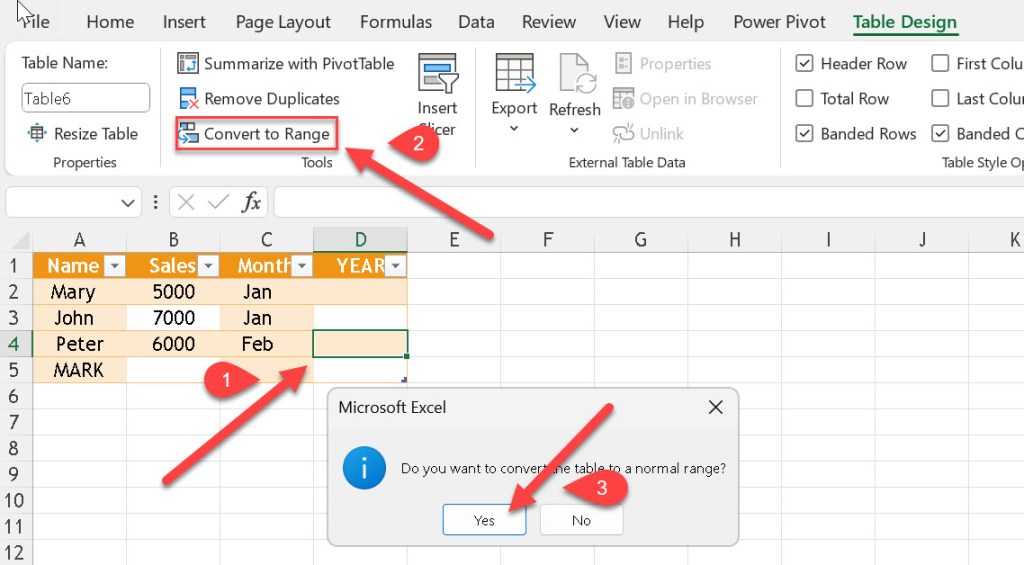
Converting Table Back to Range
- Select the table → Go to Table Design tab → click Convert to Range.
Renaming a Table
- By default, Excel names tables like Table1, Table2.
- You can rename them. Go to Table Design tab → change the name in the Table Name box.

Benefits of Using Tables in Excel
- Saves time with built-in formatting.
- Makes data analysis simpler with filters and totals.
- Improves readability with clear references.
- Automatically expands when you add more data.
- Give your work a clean, professional look.
Tables in Excel are more than just a way to make your data look neat—they bring structure to your data. By learning how to create, format and manage tables, you can work faster and smarter.